Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We are asked to find how much energy is needed to raise the temperature of a piece of iron. We will use the following formula for calculating heat energy:
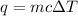
The mass of the iron is 15.0 grams. The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.45 Joules per gram degree Celsius.
The change in temperature is the difference between the final temperature and the initial temperature.
- ΔT= final temperature - initial temperature
The temperature is raised from 20.0 °C to 40.0 °C.
- ΔT = 40.0 °C - 20.0°C = 20.0 °C
Now we know all 3 variables:
- m=15.0 g
- c= 0.45 J/g °C
- ΔT = 20.0 °C
Substitute the values into the formula.
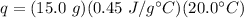
Multiply the first 2 numbers together. The units of grams cancel.
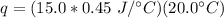
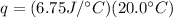
Multiply again. This time, the units of degrees Celsius cancel.
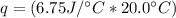
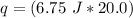
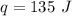
This number has 3 significant figures, which is the least number of sig fig in the original measurements, so it is the final answer.
135 Joules of energy are needed to increase the temperature of a 15.0 gram iron sample by 20.0 degrees Celsius.