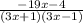Answer:
4a.
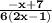
4b.
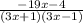
Explanation:
The expression for problem (4a) is

Least Common Multiplier of the denominators. The easiest way to do this is to simply multiply the denominators together.
LCM of
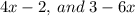
But first, let's simplify the two expressions by factoring
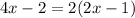 and
and
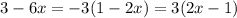

Multiply the coefficients 2 and -3 to get -6 and find an expression that appears in both.
This gives LCM as
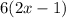
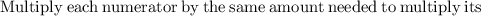
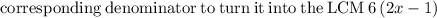
For
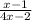
 since
since
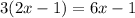
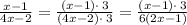
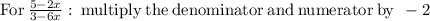 since
since
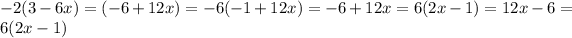
We get
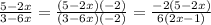
Since the denominators are the same, we can apply the fraction rule:
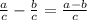
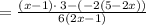
Numerator
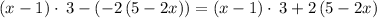 becomes
becomes
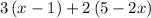 =
=
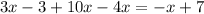
Therefore the expression result is
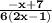
Part (b)
Note that
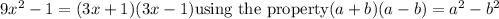
So the LCM is
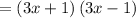 =
=
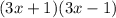
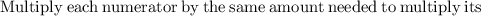
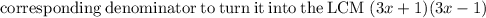
Multiply the second term in the expression by
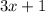 and subtract from the first term
and subtract from the first term
==>
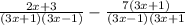
==>
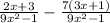
==>
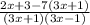
==>
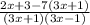
==>
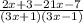
==>