Answer:
D. g(x) is a reflection of f(x) over the x-axis.
Explanation:
So when you have the equation:
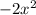 it's just negating the value of f(x), which is
it's just negating the value of f(x), which is
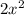 and since f(x) represents the y-value, you're negating the y-value and the x-value is unchanged. So each point on f(x) was originally: (x, f(x)) and now it's (x, -f(x)). Since the y-value is changing, it's going to be reflecting across the x-axis. So g(x) is a reflection of f(x) over the x-axis.
and since f(x) represents the y-value, you're negating the y-value and the x-value is unchanged. So each point on f(x) was originally: (x, f(x)) and now it's (x, -f(x)). Since the y-value is changing, it's going to be reflecting across the x-axis. So g(x) is a reflection of f(x) over the x-axis.