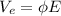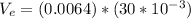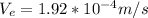Answer:
a)

b)
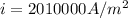
c)
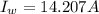
d)
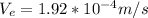
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Diameter
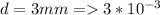
Conductivity
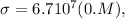
Electron mobility
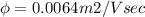
Electric field
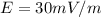
a)
Generally the equation for Charge Density is mathematically given by

Therefore
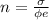
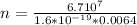

b)
Generally the equation for current density is mathematically given by
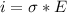
![i= 30*10^{-3] *6.7 10^7](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/57txoeuqqnj35i0z4uyvk0.png)
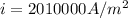
c)
Generally the equation for current in wire is mathematically given by
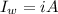
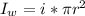
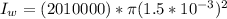
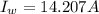
d)
Generally the equation for electron draft velocity. is mathematically given by