Answer:
a)
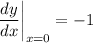
b)
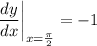
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Calculus
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/sajvvpx1sytxjokl40ke2f.png)
Derivative Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(x) + g(x)] = (d)/(dx)[f(x)] + (d)/(dx)[g(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/iqt7axoe8j2sh12ig7n0ah.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Rule [Product Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [f(x)g(x)]=f'(x)g(x) + g'(x)f(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/s9b4uuk11h1mreum0i8io5.png)
Derivative Rule [Quotient Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [(f(x))/(g(x)) ]=(g(x)f'(x)-g'(x)f(x))/(g^2(x))](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/u1jpwlo9x561ji74gvehcp.png)
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/4e7e93dqa2auubmnlpfb3w.png)
Trigonometric Differentiation
Logarithmic Differentiation
Explanation:
a)
Step 1: Define
Identify
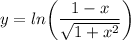
Step 2: Differentiate
- Logarithmic Differentiation [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (1)/((1 - x)/(√(1 + x^2))) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 - x)/(√(1 + x^2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/nt7147od9bx8fyy7whpqi7.png)
- Simplify:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (-√(x^2 + 1))/(x - 1) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 - x)/(√(1 + x^2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/kfb1ulm6n5wj04p4odqi33.png)
- Quotient Rule:
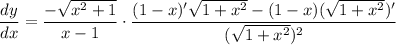
- Basic Power Rule [Chain Rule]:
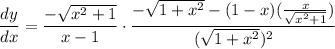
- Simplify:
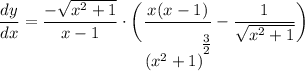
- Simplify:
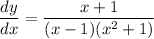
Step 3: Find
- Substitute in x = 0 [Derivative]:
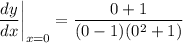
- Evaluate:
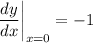
b)
Step 1: Define
Identify
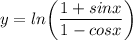
Step 2: Differentiate
- Logarithmic Differentiation [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (1)/((1 + sinx)/(1 - cosx)) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 + sinx)/(1 - cosx)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/ob5km9n4o18fza510r0i61.png)
- Simplify:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (-[cos(x) - 1])/(sin(x) + 1) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 + sinx)/(1 - cosx)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/fwbx9j24vhfdeartrzvza3.png)
- Quotient Rule:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (-[cos(x) - 1])/(sin(x) + 1) \cdot ((1 + sinx)'(1 - cosx) - (1 + sinx)(1 - cosx)')/((1 - cosx)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/9ljh2jpaz1z67bi25d1re8.png)
- Trigonometric Differentiation:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (-[cos(x) - 1])/(sin(x) + 1) \cdot (cos(x)(1 - cosx) - sin(x)(1 + sinx))/((1 - cosx)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/zxxtc4xbemj24iy0vsxkzi.png)
- Simplify:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = (-[cos(x) - sin(x) - 1])/([sin(x) + 1][cos(x) - 1])](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/cypxfjlc5zwc099uvgv3ks.png)
Step 3: Find
- Substitute in x = π/2 [Derivative]:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) \bigg| \limit_{x = (\pi)/(2)} = (-[cos((\pi)/(2)) - sin((\pi)/(2)) - 1])/([sin((\pi)/(2)) + 1][cos((\pi)/(2)) - 1])](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/o5tju2sxtevh325wx10bv5.png)
- Evaluate [Unit Circle]:
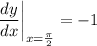
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Differentiation
Book: College Calculus 10e