Answer:
a)
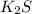 and
and
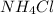 :
:
There are no insoluble precipitate forms.
b)
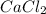 and
and
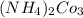 :
:
There are the insoluble precipitates of
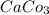 forms.
forms.
c)
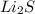 and
and
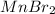 :
:
There are the insoluble precipitates of
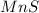 forms.
forms.
d)
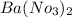 and
and
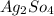 :
:
As
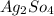 is insoluble, therefore no precipitate forms.
is insoluble, therefore no precipitate forms.
e)
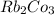 and
and
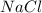 :
:
There are no insoluble precipitates forms.
Step-by-step explanation:
a)
Solubility rule suggests:-
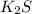 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
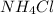 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
KCl ⇒ soluble,
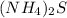 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
There are no insoluble precipitate forms.
b)
Solubility rule suggests:-
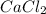 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
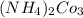 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
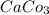 ⇒ insoluble,
⇒ insoluble,
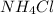 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
There are the insoluble precipitates of
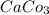 forms.
forms.
c)
Solubility rule suggests:-
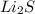 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
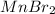 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
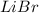 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
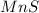 ⇒ insoluble.
⇒ insoluble.
There are the insoluble precipitates of
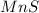 forms.
forms.
d)
Solubility rule suggests:-
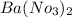 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
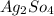 ⇒insoluble.
⇒insoluble.
As
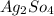 is insoluble, therefore no precipitate forms.
is insoluble, therefore no precipitate forms.
e)
Solubility rule suggests:-
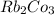 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
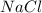 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
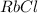 ⇒ soluble,
⇒ soluble,
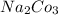 ⇒ soluble.
⇒ soluble.
There are no insoluble precipitates forms.