Answer:
Acceleration of this electron:
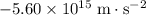 .
.
Time taken: approximately
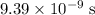 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Let
 denote the velocity of this electron before the change.
denote the velocity of this electron before the change. - Let
 denote the velocity of this electron after the change.
denote the velocity of this electron after the change. - Let
 denote the displacement.
denote the displacement. - Let
 denote the acceleration.
denote the acceleration. - Let
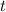 denote the time taken.
denote the time taken.
Apply the SUVAT equation that does not involve time:
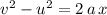 .
.
Equivalently:
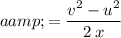 .
.
By this equation, the acceleration of this electron would be:
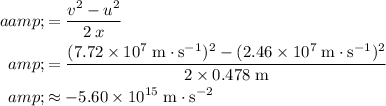 .
.
The speed of this electron has changed from
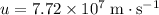 to
to
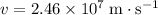 . Calculate the time required to achieve this change at a rate of
. Calculate the time required to achieve this change at a rate of
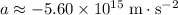 :
:
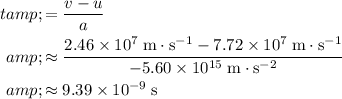 .
.