Answer:
62.5 ml of 0.032 M KMnO₄ are required to react with 50.0 ml of 0.100 molar H₂C₂O₄ in the presence of excess H₂SO₄
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced reaction is:
2 KMnO₄ + 5 H₂C₂O₄ + 3 H₂SO₄ → K₂SO₄ + 2 MnSO₄ + 8 H₂O + 10 CO₂
By stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following amounts of moles of each compound participate in the reaction:
- KMnO₄: 2 moles
- H₂C₂O₄: 5 moles
- H₂SO₄: 3 moles
- K₂SO₄: 1 mole
- MnSO₄: 2 moles
- H₂O: 8 moles
- CO₂: 10 moles
Molarity or Molar Concentration is the number of moles of solute that are dissolved in a certain volume.
The molarity of a solution is calculated by dividing the moles of the solute by the volume of the solution:
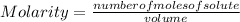
Molarity is expressed in units
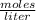
In this case, 50 mL (0.05 L) of 0.1 M H₂C₂O₄ react. So, replacing the data in the definition of molarity:
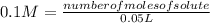
Solving:
number of moles of solute= 0.1 M*0.05 L
number of moles of solute= 0.005 moles
So, 0.005 moles of H₂C₂O₄ react. Then you can apply the following rule of three: if by stoichiometry 5 moles of H₂C₂O₄ react with 2 moles of KMnO₄, 0.005 moles of H₂C₂O₄ react with how many moles of KMnO₄?
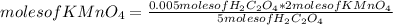
moles of KMnO₄= 0.002 moles
Knowing that the molarity of KMnO₄ is 0.032 M, replacing in its definition and solving:
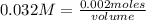
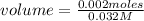
volume= 0.0625 L= 62.5 mL
62.5 ml of 0.032 M KMnO₄ are required to react with 50.0 ml of 0.100 molar H₂C₂O₄ in the presence of excess H₂SO₄