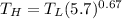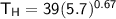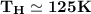Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy for an isothermal expansion can be computed as:
 --- (1)
--- (1)
However, we are being told that the volume of the gas is twice itself when undergoing adiabatic expansion. This implies that:
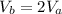
Equation (1) can be written as:
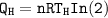
Also, in a Carnot engine, the efficiency can be computed as:
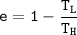
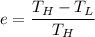
In addition to that, for any heat engine, the efficiency e =
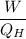
relating the above two equations together, we have:
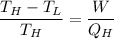
Making the work done (W) the subject:
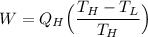
From equation (1):
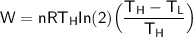
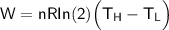
If we consider the adiabatic expansion as well:
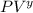 = constant
= constant
i.e.
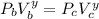
From ideal gas PV = nRT
we can have:
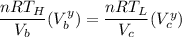
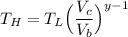
From the question, let us recall aw we are being informed that:
If the volumes changes by a factor = 5.7
Then, it implies that:
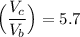
∴
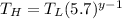
In an ideal monoatomic gas
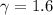
As such:
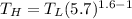
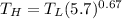
Replacing the value of
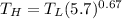 into equation
into equation
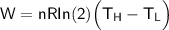
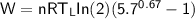
From in the question:
W = 930 J and the moles = 1.90
using 8.314 as constant
Then:
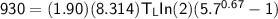
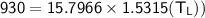
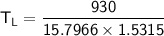
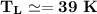
From