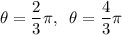Answer:
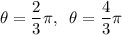
Explanation:
Given:
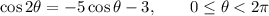

Use the cos double angle identity to create a quadratic:
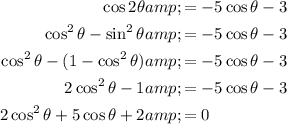
Factor the quadratic:
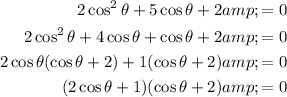
Apply the zero-product property:
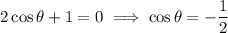

As -1 ≤ cos θ ≤ 1, cos θ = -2 is undefined.
Therefore, the only valid solution is cos θ = -¹/₂
Therefore:
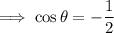
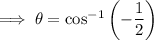
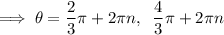
Solutions in the given interval 0 ≤ θ < 2π :