The data is missing in the question. The data is provided below :
Document : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Brand A 17 29 18 14 21 25 22 29
Brand B 21 38 15 19 22 30 31 37
Solution :
State of the hypothesis of the null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis.
Null hypothesis :
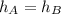
Alternate hypothesis :
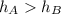
These hypothesis is a one tailed test. The null hypothesis will get rejected when the mean difference between the sample means is very small.
Significance level = 0.05
Therefore the standard error is :
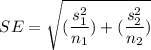
= 3.602
And the degree of freedom, DF = 14
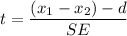
= -1.319
Here,
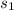 = standard deviation of the sample 1
= standard deviation of the sample 1
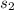 = standard deviation of the sample 2
= standard deviation of the sample 2
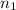 = size of the sample 1
= size of the sample 1
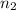 = size of the sample 2
= size of the sample 2
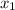 = mean of the sample 1
= mean of the sample 1
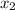 = mean of the sample 2
= mean of the sample 2
d = the hypothesis difference between the population mean
The observed difference in a sample means t static of -1.32. From t distribution calculator to determine P(
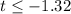 ) = 0.1042
) = 0.1042
Since the P value of 0.1042 is greater than significance level o 0.05, we therefore cannot reject the null hypothesis.
But from the test, we have no sufficient evidence that supports that Brand A is better than Brand B.