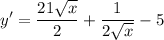Answer:
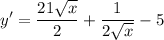
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
- Exponential Rule [Rewrite]:
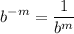
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Derivative of a constant is 0
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
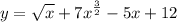
Step 2: Differentiate
- Rewrite:
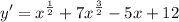
- Basic Power Rule:
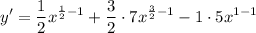
- Simplify:
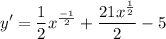
- Rewrite [Exponential Rule - Rewrite]:
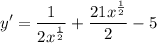
- Rewrite:
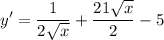
- Rearrange: