Answer:
F = 228.24 N
Step-by-step explanation:
- According Newton's 2nd Law, the impulse on one object is equal to the change in momentum of that object.
- I = F*Δt = Δp = pf - po (1)
where pf = final momentum = m*vf
p₀ = initial momentum = m*v₀
- Since after the strike, the puck reverses its direction and travels at double its speed before the strike, that means that vf = -2*v₀.
- Replacing in the right side of (1), we have:
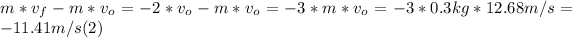
- Replacing Δt = 0.05s, and solving for F in (1):
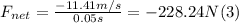
- which means that the force is applied in a direction opposite to the initial velocity of the puck.
- The magnitude of the force is just 228.24 N.