Answer
d. O₂
Step-by-step explanation
What is given:
Mass of C₄H₁₀ = 7.4 grams
Mass of O₂ = 27.8 grams
Equation: 2C₄H₁₀ + 13O₂ → 8CO₂ + 10H₂O
What to find:
To determine the limiting reactant.
Step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Determine the molar mass of C₄H₁₀ and O₂.
We shall use the atomic masses of H, C and O in the periodic table to calculate the molar mass of C₄H₁₀ and O₂.
Atomic masses of (H = 1.008, C = 12.011, O = 15.999)
Molar mass of C₄H₁₀ = (4 x 12.011) + (10 x 1.008) = 58.124 g/mol
Molar mass of O₂ = 2 x 15.999 = 31.998 g/mol
Step 2: Determine the moles of C₄H₁₀ and O₂ in 7.4 grams C₄H₁₀ and 27.8 grams O₂.
The moles of each reactant can be calculated using the mole formula below:
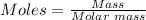
So,

Step 3: Determine the limiting reactant using the mole ratio from the given equation.
The mole ratio of C₄H₁₀ to O₂ from the given equation of reaction is 2 : 13.
This implies that 2 moles of C₄H₁₀ require 13 moles of O₂
From step 2, 1 mole of C₄H₁₀ reacted with 7 moles of O₂, therefore, O₂ is the limiting reactant.
The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely used up in a reaction and thus determines when the reaction stops.
Thus, the correct answer is option d. O₂.