Step-by-step explanation:
When a voltage V is applied across the wire of resistance R, the current I flows in the circuit. This is given by ohm's law as:
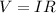
Rearranging the above equation to get the current as:
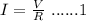
From this equation, we see that the current in the circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied and is inversely proportional to the resistance of the wire.
Now if the voltage V applied across the same wire is increased or decreased, the current I will also increase or decrease. The resistance R of the wire will remain the same as the wire is not changed.
For a long straight wire, the Ampere's law is:
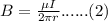
From the above equation, we see that the current I is directly proportional to the magnetic field B. This means an increase or decrease in current will cause an increase or decrease in the magnetic field.
Thus, from equations (1) and (2), we observe that the current in the wire will increase/decrease if the voltage across the wire is increased/decreased. And, this increase/decrease in the current will increase/decrease the magnetic field.
Final answer:
The magnetic field in the wire will increase/decrease, if the voltage of the battery is increased/decreased.