Answer:
An exponential function is a mathematical function, which is used in many real-world situations. It is mainly used to find the exponential decay or exponential growth or to compute investments, model populations, and so on. In this article, you will learn about exponential function formulas, rules, properties, graphs, derivatives, exponential series, and examples.
An example of an exponential formula is given below as
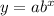
The following figure represents the graph of exponents of x. It can be seen that as the exponent increases, the curves get steeper and the rate of growth increases respectively. Thus, for x > 1, the value of y = fn(x) increases for increasing values of (n).
Are there restrictions on the domain why or why not?
For any exponential function, f(x) = ab^x, the domain is the set of all real numbers. For any exponential function, f(x) = ab^x, the range is the set of real numbers above or below the horizontal asymptote, y = d, but does not include d, the value of the asymptote.
Hence,
The domain of exponential functions is equal to all real numbers since we have no restrictions with the values that x can take.
Are exponential and logarithmic function inverse. why or why not?
Logarithmic functions are the inverses of exponential functions. The inverse of the exponential function y = a^x is x = a^y. The logarithmic function y = logx base a is defined to be equivalent to the exponential equation x = a^y
Hence,
Exponential functions and logarithmic functions are inverses of each other