Final Answer:
(a) Null Hypothesis: The completion rate among students at the certain junior college is 0.386; Alternative Hypothesis: The completion rate is less than 0.386.
(b) Symbolic Hypotheses:

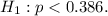
(c) Making a Type I Error: Incorrectly concluding a completion rate less than 0.386 at the certain junior college when it is 0.386 or higher.
(d) Making a Type II Error: Failing to detect a completion rate less than 0.386 at the certain junior college when it actually exists.
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The null hypothesis
 states that the completion rate for students at the certain junior college is 0.386, while the alternative hypothesis (
states that the completion rate for students at the certain junior college is 0.386, while the alternative hypothesis (
 asserts that the completion rate is less than 0.386. This sets up a one-sided test to determine if the president's belief about a lower completion rate is supported.
asserts that the completion rate is less than 0.386. This sets up a one-sided test to determine if the president's belief about a lower completion rate is supported.
(b) Symbolically, the hypotheses are represented as
 and
and
 , where
, where
 is the population proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years.
is the population proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years.
(c) Making a Type I Error involves rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. In this context, it would mean concluding that the completion rate at the certain junior college is less than 0.386 when, in fact, it is 0.386 or higher.
(d) Making a Type II Error entails failing to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative is true. In this case, it would mean not detecting a lower completion rate at the certain junior college when, in reality, it is less than 0.386. Both types of errors have implications for the accuracy of the hypothesis test and decision-making.