Answer:
-5.02 m/s (Assuming the woman's direction is the "positive" direction)
Step-by-step explanation:
The problem is a classic example of conservation of momentum where a woman jumps off a canoe and we need to find the resulting velocity of the canoe. The conservation of momentum dictates that the momentum before and after the jump remains constant, given the system is isolated.
Momentum is calculated using the formula,
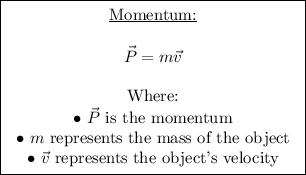

Initial System Momentum: The canoe is initially at rest, and so the initial momentum of the system (woman plus canoe) is zero.
Thus,

Final System Momentum: The momentum gained by the canoe must equal the momentum lost by the woman.

Using momentum conservation:


Thus, the canoe is traveling 5.02 m/s opposite the direction of the woman's movement.