Answer:
3.73 g of Li.
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
Volume of hydrogen gas, H2 (V) = 6.00 L.
Pressure (P) = 1.10 atm.
Temperature (T) = 25.0°C + 273 = 298 K.
R = 0.082 L*atm/mol*K.
Step-by-step solution:
First, we have to find the number of moles of hydrogen gas (H2) using the ideal gas formula:
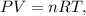
where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant and T is the temperature on Kelvin scale. So let's solve for 'n' and replace the given values:
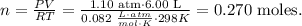
Based on this, we have 0.270 moles of H2.
You can see in the chemical equation that 2 moles of Li reacted produce 1 mol of H2, so we have to state a rule of three:
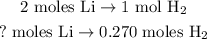
The calculation will look like this:
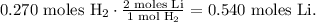
The final step is to convert 0.540 moles of Li to grams using its molar mass that can be found in the periodic table, which is 6.9 g/mol:
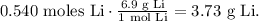
The answer is that we must use 3.73 g of Li to produce 6.00 L of H2 at 1.10 atm and 25.0 °C.