Answer:
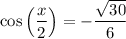
Explanation:
To find cos(x/2) given the value of sec(x) and the constraint 3π/2 < x < 2π, we can use the properties of trigonometric functions and the cosine half-angle identity.
As sec(x) is the reciprocal of cos(x), and sec(x) = 3/2, then:
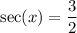
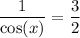
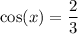
Next, we can find cos(x/2) by using the cosine half-angle identity:
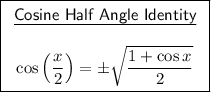
Substitute the found value of cos(x):
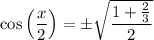
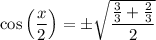
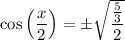
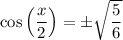
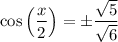
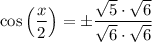
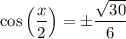
The given constraint for x is 3π/2 < x < 2π.
Therefore, the constraint for x/2 is 3π/4 < x/2 < π, which is in quadrant II. Cosine is negative in quadrant II, so we can take the negative square root:
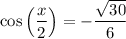
Therefore, cos(x/2) = -√(30)/6 for the given values of sec(x) and the interval 3π/2 < x < 2π.