ANSWER
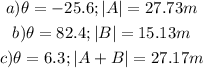
Step-by-step explanation
To find the direction of a two-dimensional vector, we apply the formula:
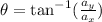
To find the magnitude of a two-dimensional vector, we apply the formula:
![|a|=\sqrt[]{(a^{}_y)^2+(a_x)^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/3vaqccbn2xy0k99xnzf0.png)
a) The direction of vector A is:
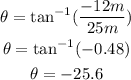
The magnitude of vector A is:
![\begin{gathered} |A|=\sqrt[]{(25m)^2+(-12m)^2} \\ |A|=\sqrt[]{625m^2+144m^2}=\sqrt[]{769m^2} \\ |A|=27.73m \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/yencnjlhkr2z7gi3s6kd.png)
b) The direction of vector B is:
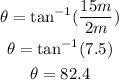
The magnitude of vector B is:
![\begin{gathered} |B|=\sqrt[]{(2.0m)^2+(15m)^2} \\ |B|=\sqrt[]{4m^2+225m^2}=\sqrt[]{229m^2} \\ |B|=15.13m \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/kipqockzw2d0dwyr6iin.png)
c) First, we have to find the sum of A and B:
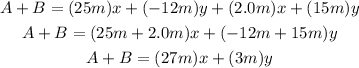
The direction of the vector (A + B) is:
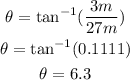
The magnitude of the vector (A + B) is:
![\begin{gathered} |A+B|=\sqrt[]{(27m)^2+(3m)^2} \\ |A+B|=\sqrt[]{729m^2+9m^2}=\sqrt[]{738m^2} \\ |A+B|=27.17m \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/icnalmx5mufwfa6gwg2j.png)