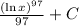EXPLANATION
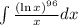
Applying subtitution: u=ln(x)
By integral substitution definition
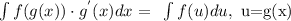
Substitute: u=ln(x)
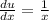
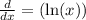
Apply the common derivative:
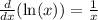
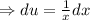
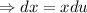
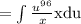
Simplify:
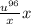
Multiply fractions:
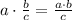
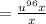
Cancel the common factor: x
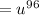
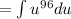
Apply the Power Rule:
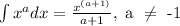
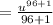
Substitute back u=ln(x)
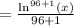
Simplify:
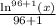
Add the numbers: 96+1=97
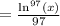
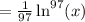
Add a constant to the solution:
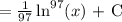
The answer is D: