The impulse exerted over an object is equal to the change in its linear momentum:
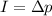
On the other hand, the impulse is equal to the force exerted over the object multiplied by the time during which the force was exerted:
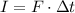
First, find the impulse by finding the change in linear momentum of the baseball. The linear momentum is given by the product of the speed of the baseball times its mass:
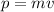
Assume that the negative direction is towards the batter and the positive direction is towards the pitcher. Then, the initial velocity of the ball is -42.3 m/s and the final velocity of the ball is 31.0 m/s. Then:
![\begin{gathered} p_i=mv_i=(0.140\operatorname{kg})(-42.3(m)/(s))=-5.922\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s) \\ \\ p_f=mv_f=(0.140\operatorname{kg})(31.0\cdot(m)/(s))=4.34\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s) \end{gathered}]()
Use the initial and final linear momentum to find the change in linar momentum, which is equal to the impulse:
![\begin{gathered} I=\Delta p \\ =p_f-p_i \\ =(4.34\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s))-(-5.922\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s)) \\ =10.262\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s) \end{gathered}]()
Isolate Δt from the equation that relates force and impulse and substitute the corresponding values for I and F to find the time during which the bat and the ball were in contact:
![\begin{gathered} \Delta t=(I)/(F) \\ =\frac{10.262\operatorname{kg}\cdot(m)/(s)}{5120N} \\ =0.00200429687\ldots s \\ \approx0.00200s=2.00ms \end{gathered}]()
Therefore, the bat and the ball were in contact during a time interval of 2 miliseconds.