So, the approximate maximum wavelength of the Hawking radiation emitted by a one-solar-mass black hole is about
 meters. This is an extraordinarily large wavelength compared to the size of the black hole, indicating extremely low-energy radiation.
meters. This is an extraordinarily large wavelength compared to the size of the black hole, indicating extremely low-energy radiation.
Given:
- Mass of the black hole,
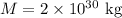
- Planck constant,

- Speed of light,
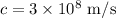
- Boltzmann constant,
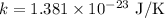
- Gravitational constant,
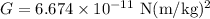
The formula for the temperature of a black hole due to Hawking radiation is:
![\[ T = (hc^3)/(16\pi^2kGM) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/2lnyy23qjfrw2qbe67y5oxf7xxkbdnp3s4.png)
Let's plug in the values and calculate the temperature:
![\[ T = \frac{(6.626 * 10^(-34) \, \text{J*s})(3 * 10^8 \, \text{m/s})^3}{16\pi^2(1.381 * 10^(-23) \, \text{J/K})(6.674 * 10^(-11) \, \text{N(m/kg)}^2)(2 * 10^(30) \, \text{kg})} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/7cih92ltar8q4d9m7g7xwmt7uiuqzg1qyi.png)
Calculating this:
![\[ T = ((6.626 * 10^(-34))(27 * 10^(24)))/(16\pi^2(1.381 * 10^(-23))(8.890 * 10^(-4))(2 * 10^(30))) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/5x4c7jp4u5s3xr7uh07vgn7irvcr22odrh.png)
![\[ T = (1.789 * 10^(-9))/(2.199 * 10^4) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/g0n5wa9698hktl5py9s2asvxa8htv150gb.png)
![\[ T \approx 8.13 * 10^(-14) \, \text{K} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/2uxd8q22b0l5q0azju2jja6i87kq7ilz0x.png)
Now, let's find the maximum wavelength of the Hawking radiation using Wien's displacement law:
![\[ \lambda_{\text{max}} = (c)/(T) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/y710s98co4yypd7cgoiw7sanj3rjrrxcb7.png)
Given:
-
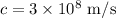
-
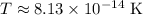
![\[ \lambda_{\text{max}} = (3 * 10^8)/(8.13 * 10^(-14)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/fpz7s1roxxsoguau14tmyjnb9sru0zlv6n.png)
Calculating this:
![\[ \lambda_{\text{max}} \approx 3.69 * 10^(21) \, \text{m} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/og1wvse7n9cvem55uexc1y8yil65lsjp4h.png)