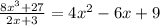The functions are given to be:
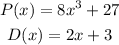
To evaluate:
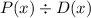
STEP 1
Divide the leading term of the dividend by the leading term of the divisor. Write down the calculated result in the upper part of the table. Multiply it by the divisor and subtract the dividend from the obtained result:
STEP 2
Divide the leading term of the obtained remainder by the leading term of the divisor. Write down the calculated result in the upper part of the table. Multiply it by the divisor and subtract the remainder from the obtained result:
STEP 3
Divide the leading term of the obtained remainder by the leading term of the divisor. Write down the calculated result in the upper part of the table. Multiply it by the divisor and subtract the remainder from the obtained result:
ANSWER