To have a constant rate of change, the function has to be a linear function of type y = mx+b.
The only function that has this form is f(x) = x/2+1, where the rate of change is m=1/2 and is constant for all values of x.
We can calculate the rate of change as:
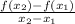
If we replace f(x2) and f(x1) we get:
![undefined]()
Answer: f(x) = x/2 + 1