ANSWER
3.79×10⁵ m/s
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
• The potential difference, ΔV = 750 V
,
• The mass of the proton, mp = 1.67*10⁻²⁷ kg
,
• The electric charge of a proton, e = 1.60*10⁻¹⁹ C
Unknown:
• The final velocity of the proton, v
The kinetic energy of the proton at the end of the motion is,
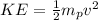
This kinetic energy is obtained from the work done to move the proton,
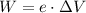
By conservation of energy,
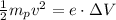
Solving for v,
![v=\sqrt[]{(2\cdot e\cdot\Delta V)/(m_p)}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/xsapz4xsgrwdjhlkh8vg.png)
Replace with the known values and solve,
![v=\sqrt[]{(2\cdot1.60*10^(-19)C\cdot750V)/(1.67*10^(-27)kg)}\approx3.79*10^5m/s](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/ykgph1mm5fmnfxn4dbx1.png)
Hence, the final velocity of the proton is 3.79 × 10⁵ m/s.