Answer:
x = -1
Explanation:
Given equation:
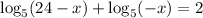
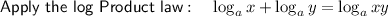
![\implies \log_5[-x(24-x)]=2](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9pmuxfn6hneogvfg8fp6.png)
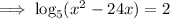
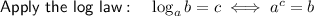
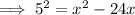
Simplify:
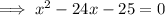
Factor the quadratic equation:
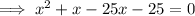

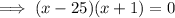
Apply the zero product property:
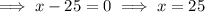
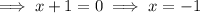
As logs of negative numbers cannot be taken, x = -1 is the only valid solution.
Check by substituting x = -1 into the original equation:
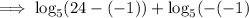
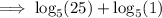
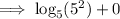
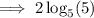
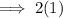
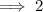
Hence, the solution is:
