Step 1
The reaction must be written, balanced, and completed:
2 MT + L(OH)2 => 2 MOH + LT2
-----------------
Step 2
Information provided:
Actual yield = 1.5 g LT2
2.6 moles MT
1.4 g L(OH)2
Molar masses of:
L(OH)2 = 54 g/mol
LT2 = 80 g/mol
-----------------
Step 3
The limithing reactant:
By stoichiometry,
2 MT + L(OH)2 => 2 MOH + LT2
2 moles MT ----------- 54 g L(OH)2
2.6 moles MT ----------- X
X = 2.6 moles MT x 54 g L(OH)2/2 moles MT
X = 70.2 g L(OH)2
For 2.6 moles of MT, 70.2 g of L(OH)2 is needed but there is only 1.4 g of L(OH)2, so the limiting reactant is L(OH)2
-----------------
Step 4
The theroretical yield: (units of it = g, like the actual yield)
By stoichiometry,
2 MT + L(OH)2 => 2 MOH + LT2
54 g L(OH)2 -------------- 80 g LT2
1.4 g L(OH)2 -------------- X
X = 2.07 g LT2 = the theoretical yield
------------------
Step 5
% yield is defined as follows:
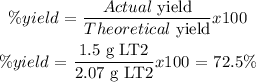
Answer: %yield = 72.5 %