The electric current in a circuit can be calculated with the formula below:
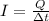
Where I is the current (in Amper), Q is the amount of charge (in Coulomb) and Delta t is the interval of time (in seconds).
That means the current is the amount of charge passing through a section in a certain amount of time.
Since the current will increase, that means the amount of charge per second passing in a section of the wire will increase.
The particles will continue to flow in the same speed, therefore what increases is the amount of charge passing in the section in the same amount of time.