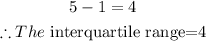1) Definition of an Outlier
An outlier is a value in a data set that is very different from the other values. That is, outliers are values unusually far from the middle.
2) Range
The range is the difference between the largest and the smallest number.
Therefore,
The largest absences = 8
The smallest absences = 1
Hence, the range is
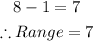
3) Interquartile range
This is calculated by subtracting the value of the first quartile from the value of the third quartile.
The formula for the first quartile is,
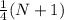
with that we get the position of our first quartile.
Firstly, we need to arrange the data given in ascending order.
Given data
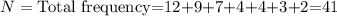
Therefore, the first quartile is
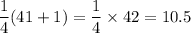
Hence, the first quartile is 1.
Let us solve for the third quartile
The formula for the third quartile is,
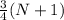
Hence, the third quartile is
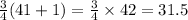
Therefore, the third quartile is 5.
Hence, the interquartile range is