Answer: considering only n = 4 and Ms = -1/2, the atom could present a maximum of 36 electrons.
Step-by-step explanation:
The question requires us to determine the maximum number of electrons for an atom with the following quatum numbers: n = 4, Ms = -1/2
The principal quantum number (n) refers to the size of an orbital. In other words, it describes how many "shells" the atom can present. If n = 4, it means that the atom presents 4 shells.
The spin quantum number (Ms) describes the angular momentum of an electron. In a simple representation, Ms describes if the arrow representing the electron points up or down. The spin quantum number can present magnitude 1/2 and direction + or -. Let's assume that +1/2 refers to "spin-up" and -1/2 refers to "spin-down".
Considering the electronic distribution given by the Linus Pauling diagram, an atom with n = 4 (and no angular quantum number, l, specified) could present the following configuration:
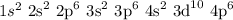
The total amount of electrons, considering only n = 4, is 36 electrons.
If we take the spin quantum number into consideration, the total amount of electrons the atom could present would not change - Ms = -1/2 means that the spin of the electron is pointing down and this electron is in an orbital which is already filled with one electron.
Therefore, considering only n = 4 and Ms = -1/2, the atom could present a maximum of 36 electrons.