The instantaneous rate of change refers to the derivative of f(x), so let's find that first, following the power rule, we have.
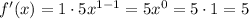
As you can observe, the instantaneous rate of change is a constant, which means we don't have to evaluate it at x=9.
Therefore, the instantaneous rate of change is f'(x) = 5.