Given:
Initial speed = 5.0 m/s
Mass of box = 1.50 kg
Final velocity = 6.5 m/s
Vertical distance = 1.5 m
Let's solve for the following:
• A) How much work does the gravitational force do on the box?
To find the amount of work done by the gravitational force, we have:
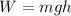
Where:
m is the mass = 1.50 kg
g is acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s²
h is the distance = 1.5 m
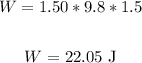
Therefore, the work done by the gravitational force on the box is 22.05 J.
• (b). How much work does the normal force do on the box?
The normal force is perpendicular to the surface.
As the block slides down the surface, there will be no normal force parallel to the motion.
Therefore, no work is done by the normal force.
• (c). What is the size of the friction force acting on the box?
To determine the frictional force acting on the box, let's first find the angle:
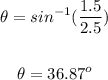
Now, find the downward force using the formula below:
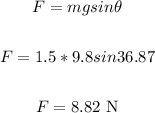
The box moves a distance of 2.5 m.
Let's find the acceleration using the motion formula:
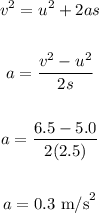
The acceleration is 0.3 m/s².
The net force is the force pushing the box downwards - the frictional force.
Hence, we have:
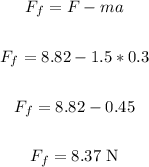
Therefore, the frictional force is 8.37 N
ANSWER:
• (a). 22.05 J
,
• (b) 0
,
• (c). 8.37 N