A terminating decimal is usually defined as a decimal number that contains a finite number of digits after the decimal point.
Usually, numbers with factors of 3 and prime numbers (numbers that are only divisible by 1 and itself) as the denominator of the fraction will have a case where the decimal does not terminate.
Let us check each option:
FIRST OPTION: 12
12 has a factor of 3. Hence it would have a non-terminating decimal.
To check, consider 1/12
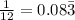
Therefore, this option is INCORRECT.
SECOND OPTION: 9
9 has a factor of 3. Hence it would have a non-terminating decimal.
To check, consider 1/9
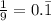
Therefore, this option is INCORRECT.
THIRD OPTION: 13
13 is a prime number. Hence it would have a non-terminating decimal.
To check, consider 1/13
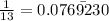
Therefore, this option is INCORRECT.
FOURTH OPTION: 16
This should always give a terminating decimal. We can check as follows:
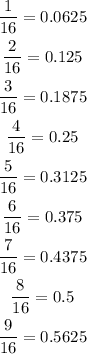
Therefore, this option is CORRECT.