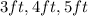The given triangle in the question is a right-angled triangle. In order to get the length of each side, we will apply the Pythagoras theorem.
The Pythagoras theorem is,
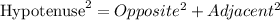
Where,
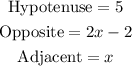
Therefore,
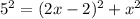
Let us expand the above
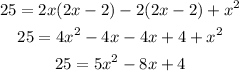
Switch sides
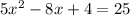
Subtract 25 from both sides
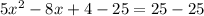
Simplify
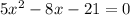
Solve with the quadratic formula
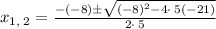
Thus
![\sqrt[]{(-8)^2-4\cdot\: 5(-21)}=22](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/txr58ttl0a7axhvc5g99.png)
Therefore,
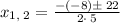
Separate the solutions
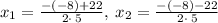
Hence,
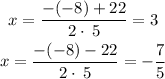
The solutions to the quadratic equations are
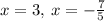
Therefore, from the above result, the length of a triangle can never be negative.
Hence, x = 3
Let us now solve the length of the remaining side
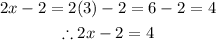
Therefore, the length of each leg is