Answer:
180 g/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
ΔT = [0 - (- 1.86 )] °C = 1.86 °C.
i = 1 (for a nonelectrolyte).
Kf = 1.86 °C/m.
Step-by-step solution:
To solve this problem, we have to use the boiling point elevation formula, which is the following:
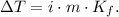
Where ΔT is the change in boiling point, i is the Van't Hoff factor, m is the molality of solution, and Kf is the molal boiling point constant.
Let's calculate the molality with the given data:
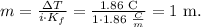
1 m is the same that 1 mol/kg. As we have 1.00 g of water and 180.0 mg of the sugar, we can multiply 1 mol/kg by the mass of water. Remember that 1 kg equals 1000 g, so 1.00 g is the same that 0.001 kg:
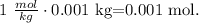
Remember that the units of the molar mass is in g/mol, and 1 g equals 1000 mg, so 180.0 mg is the same that 0.18 g. If we divide 0.18 g by 0.001 mol, we will obtain the molar mass of the sugar, which would be:
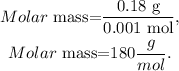
The answer would be that the molar mass is 180 g/mol.