The following assumptions are made:
1. N2 gas behaves like an ideal gas throughout the process.
2. The final pressure will be equal to atmospheric pressure.
3. The temperature remains constant.
Taking into account the above, we can apply the Boyle-Marriott Law that relates the change in pressure and volume at a constant temperature. The equation tells us:
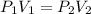
Where,
V2 is the final volume we want to find
P2 is the final pressure, atmospheric pressure= 1atm
P1 is the pressure of N2 inside the cylinder, 28.6atm.
V1 is the volume of the cylinder. To find the initial volume we will use the volume equation for a cylinder:
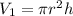
r is the radius, 4.2cm/2=2.1cm
h is the height, 17.cm
So, the volume of the cylinder will be:
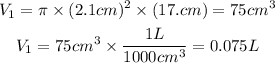
We clear V2 and replace the known data:
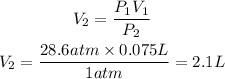
The final volume of N2 will be 2.1L
Answer: 2.1