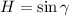Given:
Heron's formula
Sol:
Heron's formula:
for finding the area of a triangle in terms of the lengths of its sides. In symbols, if a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides
In Heron's formula is:
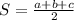
Heron's formula to find the area of a triangle is:
So, the area is:
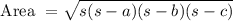
Area of triangle is :
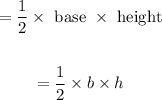
Use cosine law then:
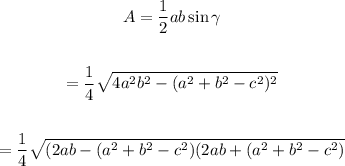
Solve then:
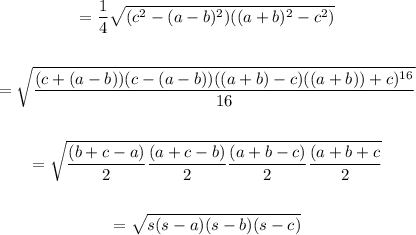
In cosine law.
Let us prove the result using the law of cosines:
Let a, b, c be the sides of the triangle and
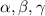
are opposite angle to the side.
We know that low of cosine is:
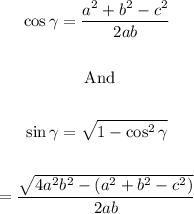
Here base of triangle = a
Height is: