Use the ideal gas law for the initial and final conditions.
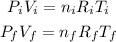
Where P_i = 10^5 N/m^2, V_i = 400 m^3, T = 10 C = 283 K. So, we have the expression about the initial conditions
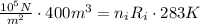
For the second expression, the final pressure and the final volume are the same because the hot-air balloon is open to the atmosphere.
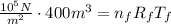
Then, use the density formula to find the initial mass and the final mass.
![\begin{gathered} m_i=\rho_iV=\frac{1.25\operatorname{kg}}{m^3}\cdot400m^3=500\operatorname{kg} \\ m_f=m_i-200\operatorname{kg}=500\operatorname{kg}-200\operatorname{kg}=300\operatorname{kg} \end{gathered}]()
Now, we find the number of moles (n) by dividing the masses.
![(n_i)/(n_f)=\frac{500\operatorname{kg}}{300\operatorname{kg}}\approx1.67]()
At last, we divide the initial equations (ideal gas law) to find the final temperature.
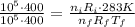
The constant R is the same in both cases and use the ratio of moles.
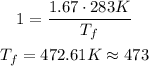
But, in Celsius, the temperature is 200 Celcius.
Therefore, the answer is D.