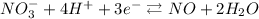To analyze what is being oxidized and reduced, we need to calcualte the oxidation number of each element.
H₂S and HNO₃ are both acids that have H as the oxidation number 1+. Also, H, in water, H₂O, also has an oxidation number of 1+. So, the hydrogen is neither being oxidized nor reduced.
In all compounds the oxigen is bonded to another element ad its oxidation number is 2- in all of them, HNO₃, NO and H₂O. So, the oxygen is neither being oxidized nor reduced.
In H₂S, the S is bonded with 2 H⁺, so its oxidation number has to be 2- so the compound is neutral. In the right side, S is alone so its oxidation number if 0.
So, each S passed from 2- to 0.
In HNO₃, N is with 3 oxygens 2- and 1 hydrogen 1+. The combined charge of the oxygens and the hydrogen is -5 (-6 from the O and 1+ from H), so the oxidation number of N has to be 5+ for the compound to be neutral.
On the right side, N is only bonded to O 2-, so its oxidation number is 2+.
So, each N passed from 5+ to 2+.
This means that each S lost 2 electrons and each N gained 3 electrons.
Thus, S is being oxidized and N is being reduced.
The half reaction of S is S with charge 2- giving S with charge zero plus 2 electrons:
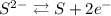
And the half reaction of N is the 6 H 1+ from H₂S HNO₃ plus the 3 electrons giving NO and H₂O.
We can right HNO₃ in its dissociated form: