Given
m: mass
m = 1.20 kg
μ: kinetic friction
μ = 0.25
vi: speed contact light spring
vi = 3.40 m/s
k: spring costant force
k = 50 N/m
Procedure
a) distance of compression
energy balance equation
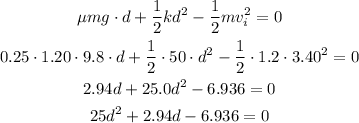
using the quadratic formula we get,
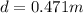
(b) find the speed v, at the unstretched
energy balance equation
![\begin{gathered} \mu mg\cdot d+(1)/(2)mv^2_i=(1)/(2)kd^2 \\ (1)/(2)kd^2-\mu mg\cdot d=(1)/(2)mv^2 \\ (1)/(2)\cdot50\cdot0.471-0.25\cdot1.20\cdot9.8\cdot0.471=(1)/(2)\cdot1.20\cdot v^2 \\ 4.1612=0.6v^2 \\ v=\sqrt[]{(4.1612)/(0.6)} \\ v=2.63m/s \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/physics/college/z27ygzofm7x8ejyzg26t.png)
(c) Find the distance D where come to rest
energy balance equation
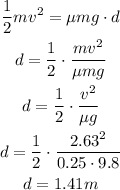
(d) What if? The object becomes attached to the end of the spring
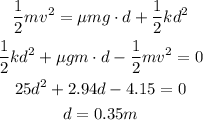
The distance would be 0.35m