Answer
The new pressure = 9 atm.
Since the new pressure of 6840 mmHg (9 atm) exceeds 6080 mmHg, then the can will likely explode.
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Initial pressure P₁ = 4 atm
Initial temperature, T₁ = 27 °C = (27 + 273.15 K) = 300.15 K
Final temperature, T₂ = 402 °C = (402 + 273.15 K) = 675.15
What to find:
The new pressure at a temperature of 402 °C.
Step-by-step solution:
According to Amonton's law: The pressure of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, provided that the volume does not change, i.e:
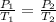
Putting P₁ = 4 atm, T₁ = 300.15 K, and T₂ = 675.15 K into the formula, we have:

The new pressure at a temperature of 402 °C = 9 atm.
According to the information in the question that the can explode if the internal pressure exerts 6080 mmHg, then we need to convert 9 atm to mmHg to know how likely is it to explode.
Conversion factor:
1 atm = 760 mmHg
So 9 atm = (9 atm/1 atm) x 760 mmHg = 6840 mmHg
Since 6840 mmHg pressure exceeds 6080 mmHg, then the can will likely explode.