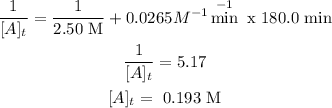The chemiacl reaction given:
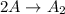
We are given that the reaction:
Is second order reaction
Have a rate constant = 0.0265M-1min-1
Initial concentration of A = 2.50 M
time = 180.0 mins
We want the concentration of A after 180.0 minutes.
For the second order reaction, we use the following equation to calculate conentrattion (integrated rate law).
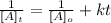
[A]t is the concentration of A at time t
[A]o is the initial concentration (at time = 0)
k is the rate constant for the reaction
Now lets plug in the values.