Given the function
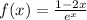
To compute the first derivative, we must recall the derivative of a quotient rule:
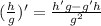
Here: h(x)=1-2x, g(x)=e^x
h'(x)=-2
g'(x)=e^x
substituting into the formula:
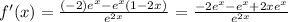
Operating:
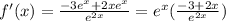
Simplifying numerator and denominator:
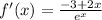
Looks like this matches the first choice
Now find the second derivative
This time: h(x)=-3+2x, h'(x)=2
g(x)=e^x, g'(x)=e^x
Applying the quotient rule again:
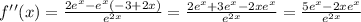
Factoring and simplifying:
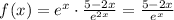
Both answers confirm the first choice is correct