If an object with mass m absorbs an amount Q of heat and increases its temperature by ΔT, the specific heat (c) of the material is defined as:
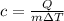
The specific heat is the amount of heat per unit mass needed to increase the temperature of a sample, per unit temperature.
Replace Q=2.34*10^3J, m=0.2kg and ΔT=30K to find the specific heat of copper:
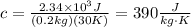
Therefore, the specific heat of copper is 390 J/(kg*K).