The first thing we have to do is to assume an ideal gas behavior, and like that, we can do our calculations.
Let's assume the two gases are nitrogen and oxygen. If we have 100 moles of the mixture, then we have 50 moles of oxygen and 50 moles of nitrogen. Then, it means that the moles' quantity is 50/50. Let's see if the mass compositions are the same:
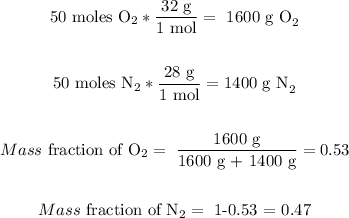
It is also approx the same split of 50/50.
Then, if we assume that the container is at 1 atm of pressure, then we can calculate the pressures of each gas:

It means that the pressure is also 50/50.
Then, if we think about the volume, remember that the gases occupy all the space that they're into. It means that both gases have the same volume, which is going to be equal to the volume of the container.
Then, the answer is volume.