Gay-Lussac's law is a law that allows us to study the behavior of gases and relates gas pressure to temperature, while other parameters such as volume and amount of substance are kept constant. Gay-Lussac's law is described by the following equation:
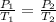
It tells us that the temperature is directly proportional to the pressure, if the temperature increases the pressure increases, and vice versa.
In a hot air balloon, once the balloon is in the air and has a constant volume, to keep the balloon in the air, the air inside the balloon is heated, which causes the pressure inside to increase while maintaining the volume constant. If the air temperature drops, the balloon will begin to fall, because the gas will escape, and the volume and pressure of the gas will decrease.