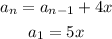Answer:
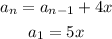
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the sequence defined by the explicit formula:
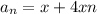
When n=1:
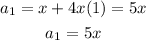
When n=2
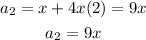
When n=3
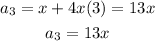
We observe that:
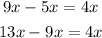
This means that to get the next term, we add 4x to the previous term.
Therefore, a recursive formula for the sequence will be: