Answer : The molar volume of the gas will be, 44.82 L
Solution :
Using ideal gas equation,
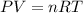
where,
n = number of moles of gas = 1 mole
P = pressure of the gas = 0.5 atm
T = temperature of the gas = 273 K
R = gas constant = 0.0821 Latm/moleK
V = volume of the gas.
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get the molar volume of the gas.
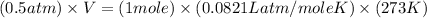
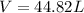
Therefore, the molar volume of the gas will be, 44.82 L